The term ‘Landsknechts’ appeared in the German language around 1470, meaning “servant of the land”, as it was formed by Maximilian I, Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, around the same time. Maximilian was impressed with the tactics displayed by the Swiss pikemen in their battle for independence against the Duchy of Burgundy and his own Empire, so he decided to copy them.
The Landsknechts continued the mercenary habits of the Swiss, which meant they became in demand. They lacked permanent political commitment and were not tied to the Reich, which meant they were only bound to those who could afford to hire them. They were hired by many noblemen to solve their quarrels, which consequently meant that the Holy Roman Empire became a battleground for squabbles between minor nobles.
They were, however, also involved in many wars, including revolts in the Netherlands, Swiss and Swedish independence uprisings, the Italian Wars (1494-1559), Peasants’ War (1524-25), Landshut War of Succession (1504), Siege of Vienna (1529), Spanish Conquest of the Americas, and 16th Century religious wars. They also carried out the violent Sack of Rome in 1527, leading to the death of one of their most famous commanders, Georg von Frundsberg.
Who could join the Landsknechts and what was the hiring process?
The call to arms for the Landsknechts attracted ‘unchristian, God-forsaken folk,’ but troops were made up of various types of people, such as peasants, artisans, nobles and criminals. However, the entrance was not automatic, as letters of articles of obligations (capitularies) between Henry VIII and Maximilian Count of Buren (contracted by Henry in 1544 to bring two thousand footmen to serve Henry in the Boulogne campaign) asserted that the troops be “well-disciplined and equipped” for war.
Furthermore, it was expected of the troops to be loyal to the king and officers, and they were forbidden from violating women, clerics and churches. Any private feuds they had, had to be laid aside until completion of the mission, as quarrelling amongst each other or allies was prohibited. Cowardice and desertion were punishable by death, and gambling, drunkenness, selling of spirits during divine service and womanising were verboten.
The steps to hiring the Landsknecht were as follows:
- Find a leader for recruits to look up to, but this could not be just anyone, the leader had to be experienced with an established reputation and accomplishments.
- This leader would then enter negotiations with the employer to agree upon terms of service.
- From these negotiations, a contract of capitularies was created.
- The leader would then have to obtain written permission and passports from princes of whose state he planned to recruit. If an applicant met the requirements stipulated in the capitularies, his personal information and speciality were stored on a muster roll. He would then be given “conduct money” and informed of the place where the regiment would assemble and the date by which he had to present himself.
- During the assembly, the men would be separated into groups. Then the lieutenant, chaplain, company quartermaster and surgeon were introduced (in that order). Two corporals (Gemeinweibel), a leader (Führer), and a Fourier were then elected by the men themselves, and these elections were presided over by the colonel’s appointee, the sergeant (Feldweibel). After this, ensigns were divided into files of 16, and each one elected its own leader (Rottenmeister).
Uniform, Weapons, and Tactics
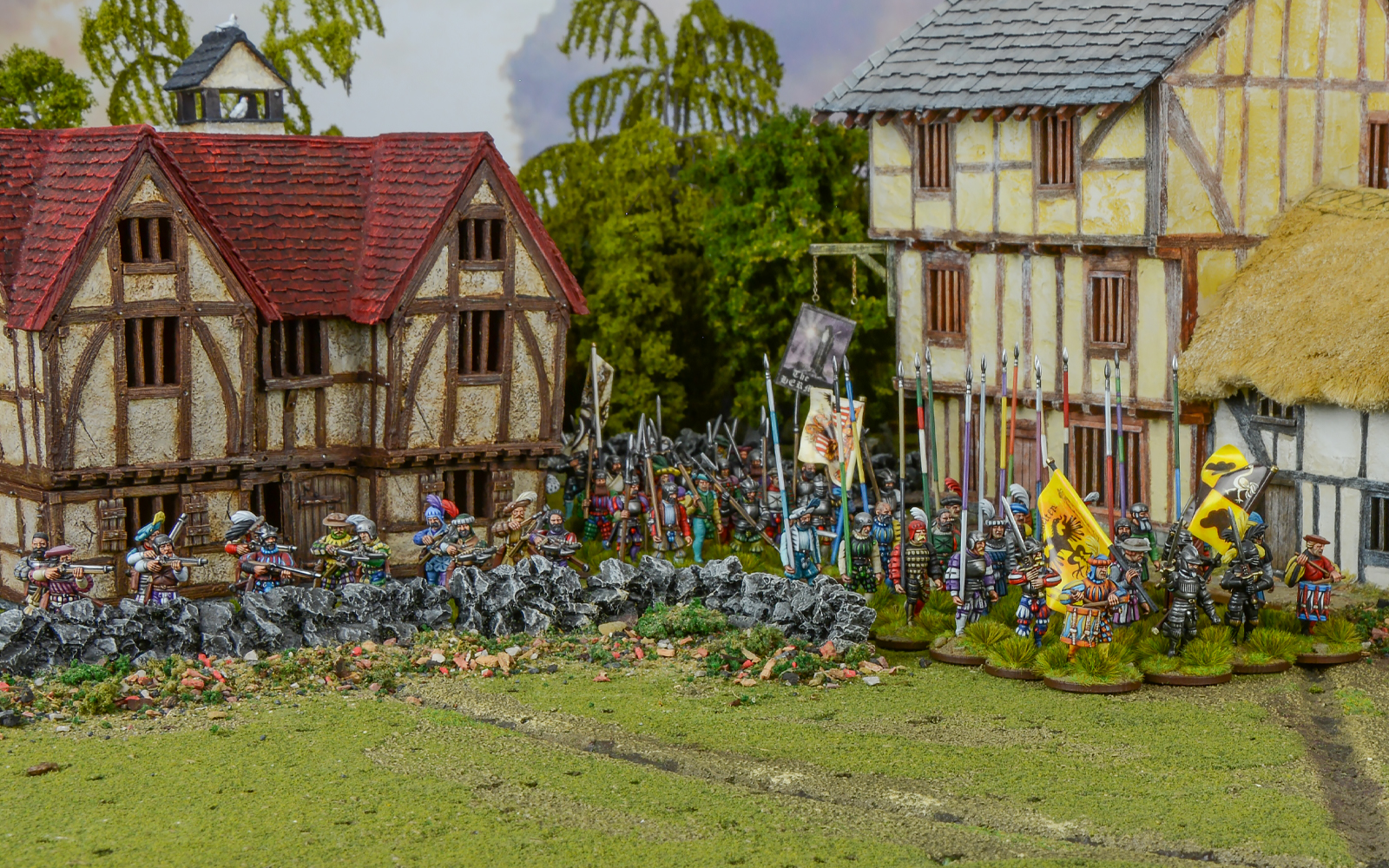
The Landsknechts wore brightly coloured rags with brightly covered feathers, which were taken from their opponents. Because of this, their clothes did not fit properly and were torn and tied. They wore the most garish costumes they could devise, such as slashed doublets, striped hose, tight or wide breeches and outrageous codpieces. These garments flaunted their status, intimidated enemies, and shocked civilians. The Landsknecht were said to be a “fearsome sight to behold.” Armour was rarely worn, but when it was it consisted of a breastplate with tassets and a steel skull cap worn under a wide-brimmed cap. The soldiers only had these clothes, with nothing else to change into. This meant that they had to constantly steal clothing from those they defeated, but some chose not to, in an attempt to intimidate enemies even more – preferring to always present themselves as battle-worn and hardened. The reason for such a bright and shocking dress code was Maximilian I’s ruling at the Diet of Augsburg in 1503. He said that the troops deserved at least one luxury (food, water and resources were scarce), so they could wear what they wanted.

The main weapon in the Landsknechts was the pike; used alongside glaives, halberds, axes, broadswords, short-swords and maces. The weapon of choice for the Doppelsöldner, who fought in the front rank to charge against enemy pikemen (one of the more dangerous positions, so they were paid twice as much), was the Zweihänder sword. It was an up-to 66-inch-long sword with a double-edged and sometimes rippling blade, weighing anywhere between 7 to 14 pounds. Initially, crossbows were used but they were replaced by arquebuses, which were muzzle-loading rifles with a simple matchlock. When the trigger was pulled, the serpentine arm holding the lit cord was plunged into the powder pan, igniting the powder inside and firing the shell. While the weapon was heavy and typically fired from a rest, the Landsknechts, as a matter of pride, would often use them without one.
In battle, the troops would form an Igel (hedgehog) position. This consisted of a huge square of pikemen (up to 4000 strong) surrounded by double ranks of halberdiers, swordsmen and arquebusiers, presenting the enemy with an unstoppable object that was impenetrable to protect hand-gunners but offensively trampled everything in its path. Another position used was the Verlorene Haufe (forlorn hope) position, which involved a thin line of double-handed swordsmen and halberdiers that would charge at an opposing Igel formation, darting in between enemy pikes to break up their ranks. This position was only taken on by volunteers who wanted glory or redemption, and they took a red banner to fight under, as the position was almost always fatal.
Camp Life
A Landsknecht force on the march proved an impressive logistical feat in each instance. Along with thousands of mercenaries came their gear, supplies and equipment, with their many followers, travelling miles on foot.
Included in the camp Tross were the Kampfrau, who acted as nurses, cooks, cleaners and companions, as well as common labourers, merchants, families of the mercenaries, animals, thieves and scavengers. The camp was unruly itself so even require its own police force, known as the Hurenweibel.
Italian Wars
The Landsknechts were heavily involved in the Italian Wars, which were a series of violent wars for control of Italy between 1494-1559. It was fought largely by France and Spain but involved much of Europe. In 1494 French King Charles VIII invaded Italy and took Naples, but the allegiance between Maximilian I, Spain and the Pope drove him out.
In 1525, under the rule of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, the Landsknechts captured the new French King Francis I, forcing him to sign the Treaty of Madrid and renouncing all claims to Italy, but after he was freed he went back on his word and formed an allegiance with Henry VIII. This led to the Sack of Rome in 1527, resulting in the death of Georg von Frundsberg, forcing Francis I to give up the claim to Italy in the Treaty of Cambrai. The war finally ended with the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559.
Now you can relive the battles of these colourful, fearsome mercenaries!
Article by Jess Webb
The Landsknechts on the Battlefield
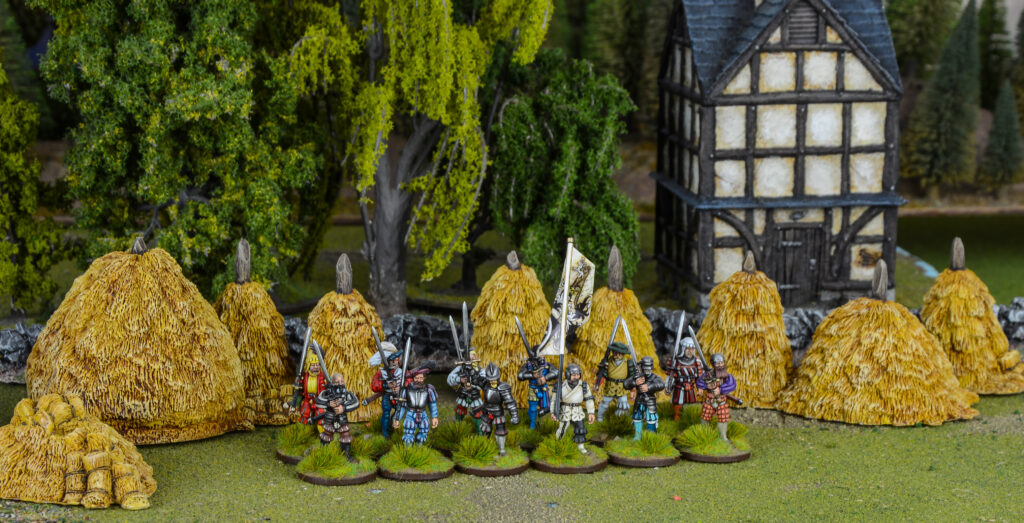
Now that you’ve been inspired, it’s time to put the Landsknechts onto the battlefield, and there’s no better way than using these beautifully crafted models.
Or perhaps you’ve already got your starter set or starter army and you’re looking to fill out your new Landsknect Army with key units?
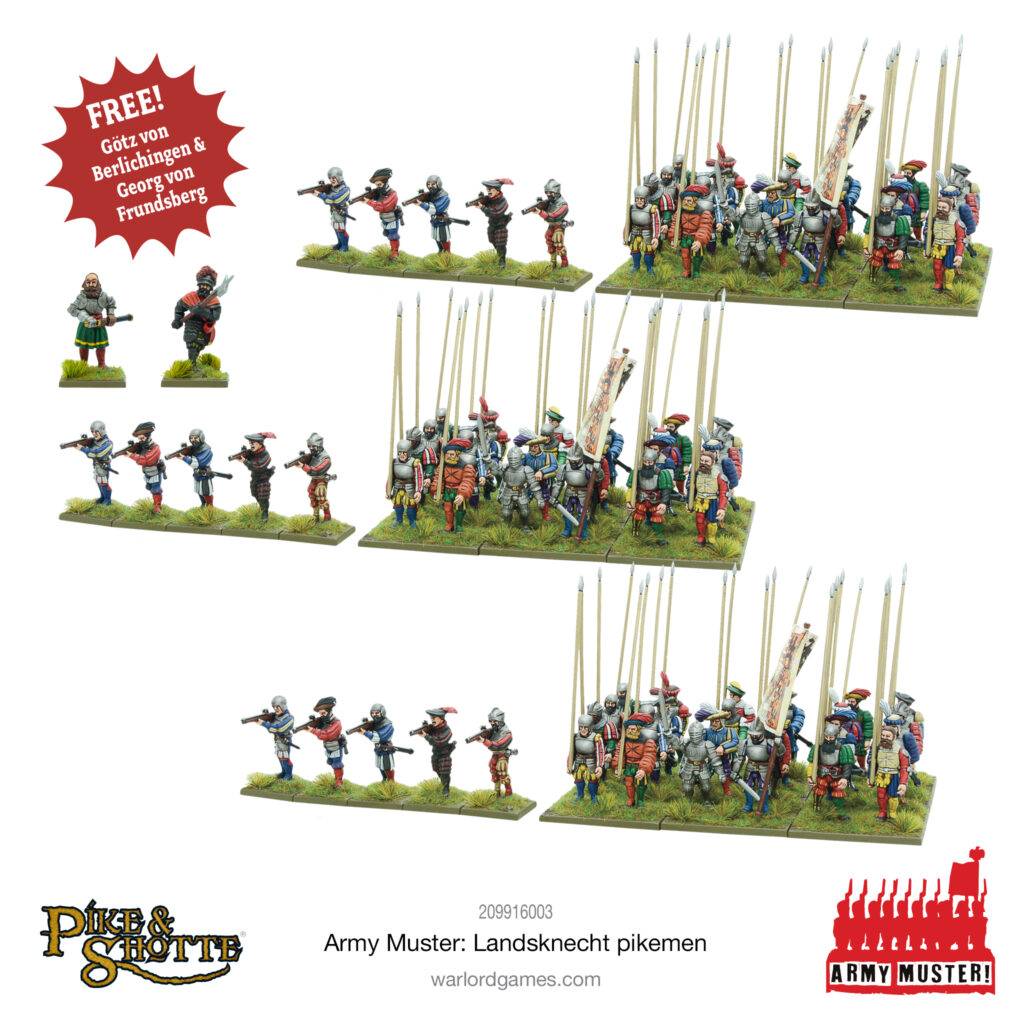
Army Muster is a brand new set of bundles tailored to those all-important core units in our mass-battle historical wargames. An easy way to expand existing and new collections alike, each Army Muster bundle contains three copies of one of our plastic boxed sets, plus a complementary product that will support your new soldiers nicely on the tabletop.













